CAREER PATHS
Certified Nurse Midwives vs. Nurse Practitioners: Clarifying the Distinctions
-
 EveryNurse Staff
EveryNurse Staff
- Last Updated: 05/28/2023

The healthcare industry is filled with various healthcare professionals and providers that offer a wide range of services. Among these healthcare professionals are Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) and Nurse Practitioners (NPs). Both professionals provide patient care, but they differ in their roles, responsibilities, education, and training.
This article aims to clarify the distinctions between them, their scope of practice, specialties, salaries, and job outlook to help individuals interested in pursuing a career in healthcare make informed decisions.
Understanding the Roles: Certified Nurse Midwives and Nurse Practitioners
Both CNMs and NPs are advanced-practice registered nurses (APRNs) who have gone through formal education and training programs that allow them to provide specialized care to patients. However, their roles and responsibilities differ slightly, as they have different areas of expertise.
The Role of a Certified Nurse Midwife
Certified Nurse Midwives are APRNs who specialize in taking care of women’s reproductive health, specifically during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. They play a crucial role in the healthcare system by providing support and guidance to women during one of the most important and vulnerable times in their lives.
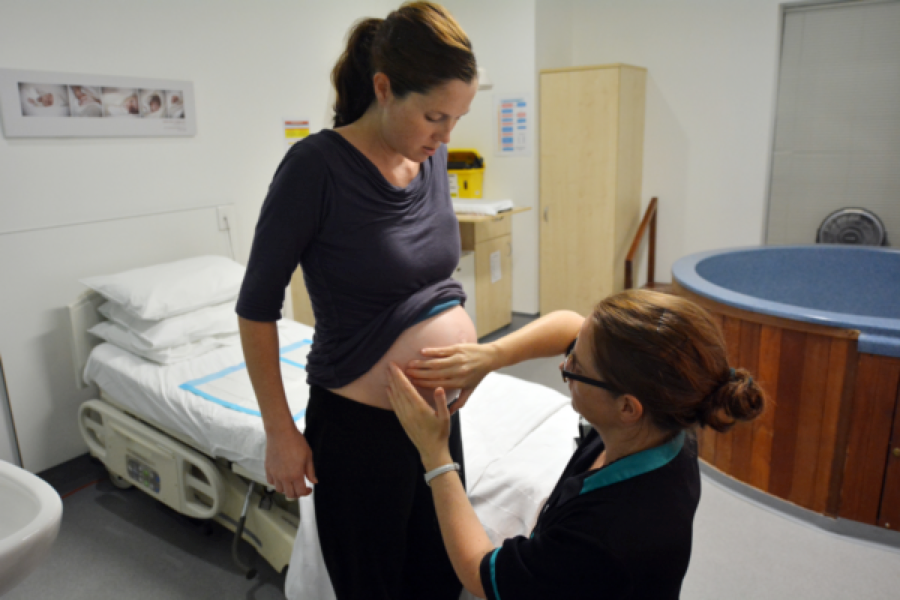
During pregnancy, CNMs work closely with expectant mothers to ensure that they receive the appropriate care and support needed for a healthy pregnancy. They monitor the mother’s health and the growth and development of the fetus, and they provide education and guidance on topics such as nutrition, exercise, and childbirth preparation.
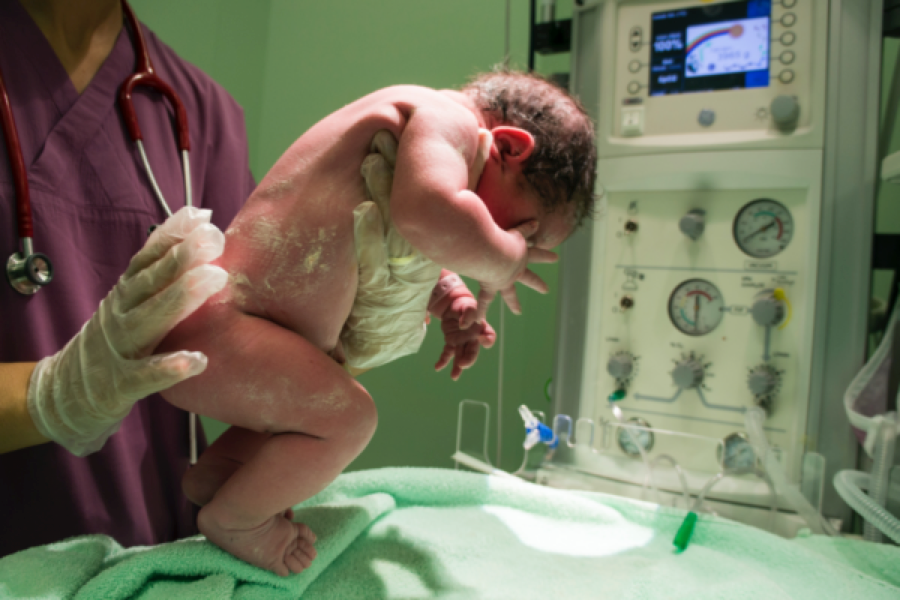
During childbirth, CNMs are trained to provide a range of services, including pain management, delivery assistance, and postpartum care. They work closely with physicians and other healthcare professionals to ensure that the mother and baby receive the best possible care.
After childbirth, CNMs continue to provide care to new mothers and their babies, monitoring their health and providing support and education on topics such as breastfeeding, infant care, and postpartum recovery.
In addition to their work with pregnant and postpartum women, CNMs also provide primary healthcare services to women of all ages. They offer a full range of gynecological and obstetric services, including family planning, pap smears, and breast exams. They also provide counseling and education on topics such as contraception, sexually transmitted infections, and menopause.
The Role of a Nurse Practitioner
Nurse Practitioners are APRNs who provide comprehensive healthcare services to patients of all ages, from infants to seniors. They play a critical role in the healthcare system by providing primary care services to patients who may not have access to a physician or who need more specialized care.
NPs are trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of illnesses and conditions, from minor illnesses such as the flu to chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. They also provide preventive care services, such as immunizations and health screenings, and they work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that address their unique needs and concerns.
In addition to their clinical work, NPs also play an important role in patient education and counseling. They work with patients to identify and manage risk factors for chronic diseases, such as obesity and smoking, and they provide education and support on topics such as nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
Education and Training Requirements
The education and training programs for Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) and Nurse Practitioners (NPs) are rigorous and require a significant amount of time and effort to complete.
Certified Nurse Midwife Education and Training
To become a CNM, you must hold a bachelor’s degree in nursing and a Master’s degree in Nurse-Midwifery. The Master’s degree program in Nurse-Midwifery includes courses in maternal and fetal physiology, antepartum and postpartum care, neonatal care, pharmacology, and ethics.
During their education and training, CNMs learn how to provide comprehensive care to women throughout their reproductive lives. They are trained to identify and manage common complications that may arise during pregnancy and childbirth, and they work closely with obstetricians and other healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
After completing their education and training, CNMs must pass a national certification exam to become licensed to practice. This rigorous exam tests their knowledge and skills in all areas of midwifery practice, including prenatal care, labor and delivery, and postpartum care.
Nurse Practitioner Education and Training
To become an NP, you must hold a bachelor’s degree in nursing and a Master’s degree in Nursing, Family, Pediatrics, or Adult-Gerontology. The Master’s degree program in nursing includes courses in pharmacology, pathophysiology, health assessment, patient education, and clinical practicum.
During their education and training, NPs learn how to provide comprehensive care to patients across the lifespan. They are trained to diagnose and manage common acute and chronic illnesses, order and interpret diagnostic tests, and prescribe medications. NPs also provide health promotion and disease prevention services, and they work closely with other healthcare professionals to coordinate care for their patients.
After completing their education and training, NPs must pass a national certification exam to become licensed to practice. This exam tests their knowledge and skills in all areas of primary care practice, including health promotion, disease prevention, and management of acute and chronic illnesses.
Scope of Practice and Responsibilities
While both CNMs and NPs are skilled and highly trained healthcare professionals, their areas of expertise and patient focus vary significantly. CNMs specialize in providing comprehensive care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum periods, with an emphasis on reproductive and maternal health. On the other hand, NPs have a broader scope that encompasses primary and specialty care across different populations and age groups.
Scope of Practice for Certified Nurse Midwives
The scope of practice for Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) encompasses a specialized and essential role in women’s healthcare. As advanced practice registered nurses, CNMs have a distinct focus on providing comprehensive care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period.
Their expertise extends beyond obstetrics to encompass gynecological care and primary healthcare services for women throughout their lifespan. With a holistic and patient-centered approach, CNMs play a vital role in promoting maternal health, ensuring safe deliveries, and supporting women’s overall well-being. Their scope of practice includes:
- Performing vaginal exams, cervical exams, and breast exams: CNMs perform routine exams to assess the health of their patients’ reproductive system. These exams can help detect early signs of cancer or other abnormalities.
- Monitoring fetal development and providing prenatal care: CNMs provide comprehensive prenatal care to expectant mothers, including regular check-ups, ultrasounds, and other diagnostic tests to monitor the health of the developing fetus.
- Performing and managing labor and delivery: CNMs are trained to provide safe and effective care during labor and delivery. They can administer pain relief medications, monitor the progress of labor, and perform emergency procedures if necessary.
- Providing postpartum care, including breastfeeding support: CNMs provide postpartum care to new mothers, including guidance on breastfeeding, postpartum depression screening, and management of postpartum complications.
- Providing contraceptive services and counseling: CNMs provide counseling on various contraceptive methods and can prescribe and administer contraceptives to their patients.
- Providing menopause and perimenopause management: CNMs can provide counseling and prescribe medications to women experiencing menopause or perimenopause symptoms.
Scope of Practice for Nurse Practitioners
Nurse Practitioners (NPs) have a broad and vital scope of practice that encompasses primary and specialty care across diverse patient populations. As advanced practice registered nurses, NPs are highly trained to diagnose and treat acute and chronic illnesses, order and interpret diagnostic tests, prescribe medications, and provide health promotion and disease prevention counseling. Their scope of practice includes:
- Diagnosing and treating acute and chronic illnesses: NPs can diagnose and treat a wide range of acute and chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma.
- Ordering and interpreting diagnostic tests, such as laboratory tests and imaging scans: NPs can order and interpret various diagnostic tests to help diagnose and manage their patients’ health conditions.
- Prescribing medications and managing patient medications: NPs can prescribe medications and manage their patients’ medications as part of their treatment plan.
- Providing preventive care and health education, such as smoking cessation and stress management: NPs can provide preventive care services to their patients, such as immunizations, cancer screenings, and health education on various topics.
- Referring patients to other healthcare professionals if necessary: NPs can refer their patients to other healthcare professionals, such as specialists or surgeons, if their patients require specialized care.
Work Settings and Specializations
Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) and Nurse Practitioners (NPs) have diverse work settings and opportunities for specialization within their respective roles. CNMs often work in hospitals, birthing centers, and women’s health clinics, focusing on providing care during pregnancy, childbirth, and women’s reproductive health.
NPs, on the other hand, have a broader scope of practice and can work in various settings such as primary care clinics, hospitals, specialty clinics, and community health centers, specializing in areas such as family practice, pediatrics, geriatrics, mental health, and more. These varied work settings and specializations allow CNMs and NPs to address the unique healthcare needs of different populations.
CNM and NP Salaries and Job Outlook
Both CNMs and NPs enjoy competitive salaries and strong job prospects. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for nurse practitioners was $124,680 in May 2022, while certified nurse midwives earned a median annual wage of $122,450. The job outlook for both CNMs and NPs is also favorable, with a projected growth rate of 46% and 7% respectively. The increasing demand for healthcare services, emphasis on preventive care, and expanded scope of practice for NPs contribute to this positive job outlook.