Community Health Nurse
-
 EveryNurse Staff
EveryNurse Staff
- Last Updated: June 23, 2023
Community health nurses work to improve the health and well-being of the communities they serve by educating them about illness, disease prevention, safe health practices, and how to obtain health care services. They also facilitate communication between people, their families, and the medical community to improve health outcomes in vulnerable communities.
Community health nurses are instrumental in creating programs that allow communities to become healthier and often provide treatment for poor, culturally diverse, and uninsured populations. Their work may include free health care screenings, vaccinations, and other preventative care at reduced costs.
What Is a Community Health Nurse?
A Community Health Nurse (CHN) is a registered nurse (RN) who promotes health for diverse communities, infants, children, adolescents, and adults. One of the primary roles of community health nurses is to identify community health problems and provide direct care to patients and vulnerable populations who may not have access to health care or cannot afford medical services.
CHNs develop intervention plans to address individuals’ and communities’ health, safety, and quality of life needs. They may also identify health concerns that impact a specific population, conduct community assessments to identify potential problems and develop or implement various health promotion and health education programs.
What Does a Community Health Nurse Do?
In addition to the traditional role of providing direct patient care in a clinical setting, Community Health Nurses (CHNs) work to educate and empower individuals and groups to take responsibility for managing their health. They often serve in community health centers and clinics as public health education resources about specific diseases or conditions, like the importance of breast cancer screening or the dangers of smoking.
CHNs collaborate with other health professionals, educators, government agencies, and community members to plan and implement community-level public health initiatives that address social determinants of health. These nurses are an essential resource for families, educators, and patients and help better understand community health issues.
Community Health Nurse Job Description
Community health nurses play a vital role in the following:
- Educating communities about healthy lifestyles and disease prevention.
- Providing in-home treatment and support services to individuals and families who need them. This can include blood pressure monitoring, pain management, medication administration, and wound care.
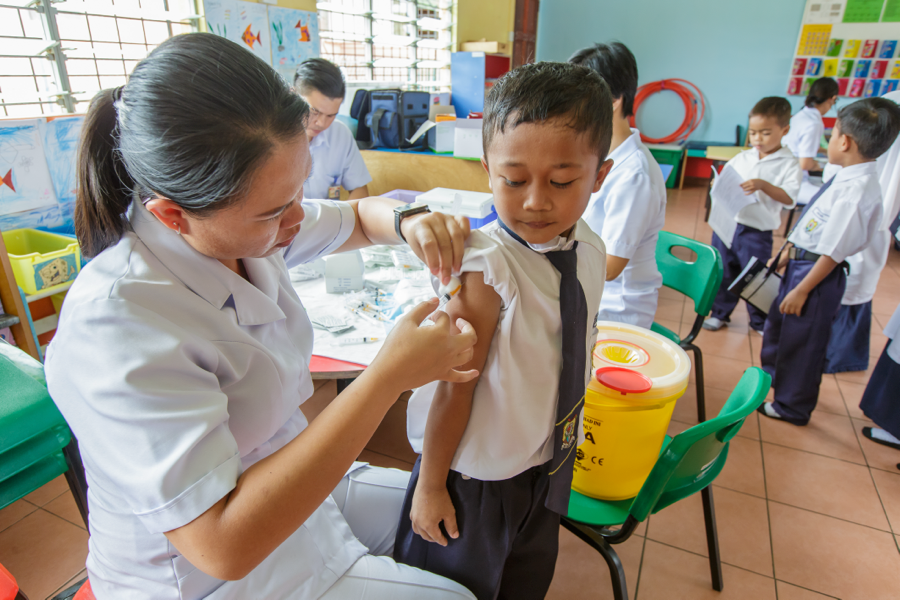
- Performing free health screenings for common diseases, including obesity, diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and other chronic health problems.
- Conducting health assessments to identify risk factors for chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease.
- Counseling people at increased risk of illness or injury about taking precautions to prevent illness, including performing screenings that lead to early disease detection.
- Describing how insurance works and helping uninsured or underinsured people gain access to healthcare services.
- Participating in community outreach by distributing public health information at schools, churches, workplaces, and other community settings.
- Educating the public about health and safety measures during and after natural disasters. They provide information on sanitation, clean water access, disease prevention, and psychological support to help alleviate the impact of the disaster on the community’s well-being.
The Importance of Community Health Nurses
Community health nursing is a vital part of the healthcare system. The CDC reports that 6 in 10 adults in the U.S. suffer from health problems that originate from chronic conditions and diseases acquired in the community, such as obesity, heart disease, and cancer. By working within the community, CHNs provide services for these conditions while helping to educate people on how best to prevent them.
The work of CHNs is vital in rural areas, medically underserved populations, and economically disadvantaged communities. Many people in these areas lack access to affordable healthcare options and educational support to help them maintain good health. CHNs help fill this void by providing care and nursing education to the poor, uninsured, and those with low health literacy.
Community Health Nurse Roles
There are many subfields of community health nursing, including public health nursing, school nursing, women’s health, occupational health nursing, and pediatric nursing. Nurses in these areas all play a part in preventing illness, health promotion, and addressing disparities in the community. CHNs often specialize in one or more of the following roles:
School Nurse
The unique focus of a school nurse makes them one of the most recognizable community health nurses. Their primary focus is the health and safety of a school community and managing healthcare emergencies in a school setting. The role is essential in ensuring that children are protected from preventable diseases, have access to appropriate healthcare services for injury or illness, and receive education about healthy lifestyle choices.
Behavioral Health Specialist
Mental illness is often stigmatized, but it can affect anyone at any time. Community health nurses who specialize in behavioral health work closely with individuals to assess their mental and emotional states to identify possible issues related to depression, anxiety, or other mental illnesses.
Behavioral health specialists are trained to provide mental healthcare services in schools, homes, or other community settings. They are often hired by schools that have a high population of children who face emotional, behavioral, or mental challenges. Their role involves teaching parents and teachers how best to support the child’s needs, implementing behavior management techniques at home and school, providing support during psychiatric emergencies, and helping coordinate healthcare and social services.
Occupational Health Nurse
Occupational health nurses promote public health by reducing hazards in the workplace. They may work with employers to create healthy office spaces, train new employees to decrease injuries or risks, advise other healthcare professionals about preventative services, or analyze injury reports for patterns that could indicate a safety issue.
Women’s Health Nurse
Pediatric Nurse
A pediatric nurse works with children to promote healthy growth and development. They may work in the maternity ward of a hospital or an outpatient clinic or be employed by schools as part of the school health staff. Pediatric nurses care for children from birth to adolescence, including care during physical exams and treating minor injuries or illnesses. They also educate children about disease prevention, nutrition, and other lifestyle behaviors that can help them stay healthy.
Clinical Research Nurse
Clinical research nurses are the link between healthcare providers and clinical trial researchers. They recruit study participants, work with patients through every step of the trial process, maintain patient records, and help ensure that clinical trials run smoothly to collect reliable data for use in research studies. Hospitals, clinics, or academic institutions often employ them.
Community Health Nurse Certification
Registered nurses actively involved in the community are eligible to become certified as Community Health Nurses (CHN). A certification in Community Health Nursing is available through the American Nurses Credentialing Center and is awarded to nurses who meet specific requirements.
Nurses who have earned this certification are prepared to work across disciplines, focusing on promoting health and wellness within communities. Nurses with this professional credential are recognized as leaders in the community health field, improving their professional status and chances for career growth and advancement.
Community Health Nurse Salary
Community health nursing is an area of specialization for registered nurses (RNs), meaning their salaries are generally similar to that of other RNs. According to employment and wage data published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the mean annual wage for registered nurses across various specialties was $89,010 in May 2022.
Registered nurses in the bottom 10% of all earners reported salaries of approximately $61,250, while those in the top 10% earned more than $129,400 annually. These salary figures are based on over 500,000 RNs who responded to the BLS survey.
| STATE | HOURLY MEAN WAGE * | ANNUAL MEAN WAGE * |
|---|---|---|
| Massachusetts | $33.82 | $70,346 |
| Alaska | $31.93 | $66,413 |
| Nevada | $31.68 | $65,888 |
| Washington | $31.16 | $64,815 |
| New York | $30.31 | $63,038 |
| Maryland | $30.24 | $62,908 |
| Nebraska | $29.67 | $61,704 |
| New Hampshire | $29.29 | $60,915 |
| Virginia | $29.28 | $60,895 |
| Colorado | $28.64 | $59,577 |
| * Zip Recruiter, Average Public Health Nurse Salary By State, November 2021 | ||
Community Health Nurse Resources
- National Association of Community Health Centers (NACHC)
- Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations (AAPCHO)
- Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
- National Association of County and City Health Officials
- National Rural Health Association
- Association of Community Health Nursing Educators (ACHNE)
- Association of Public Health Nurses
- Council of Public Health Nursing Organizations
- American Public Health Association
Community Health Nurse FAQ
What is the difference between a community health nurse and a public health nurse?
Community health nurses and public health nurses work closely together with an aligned goal to help underserved communities. Community health nurses advocate for people within communities that need access to quality healthcare. They engage local governments and healthcare facilities to ensure these individuals receive equitable access to the necessary care. Public health nurses review scientific studies and data specific to populations and tend to work for government agencies. They focus on controlling infectious diseases through public education and programs.
What qualifications do I need to be a community health nurse?
The first step is completing a nursing program (associate degree or bachelor’s degree), ideally in a program with courses focused on public health policy. From there, you must pass your NCLEX-RN in the state you want to practice in. Some aspiring community nurses earn a Master’s in Public Health to serve better the communities they hope to help. The ANCC offers an Advanced Public Health Nurse-Board Certified (APHN-BC) credential, which requires you to be licensed to practice in the state and a graduate degree in public health sciences or community health.



